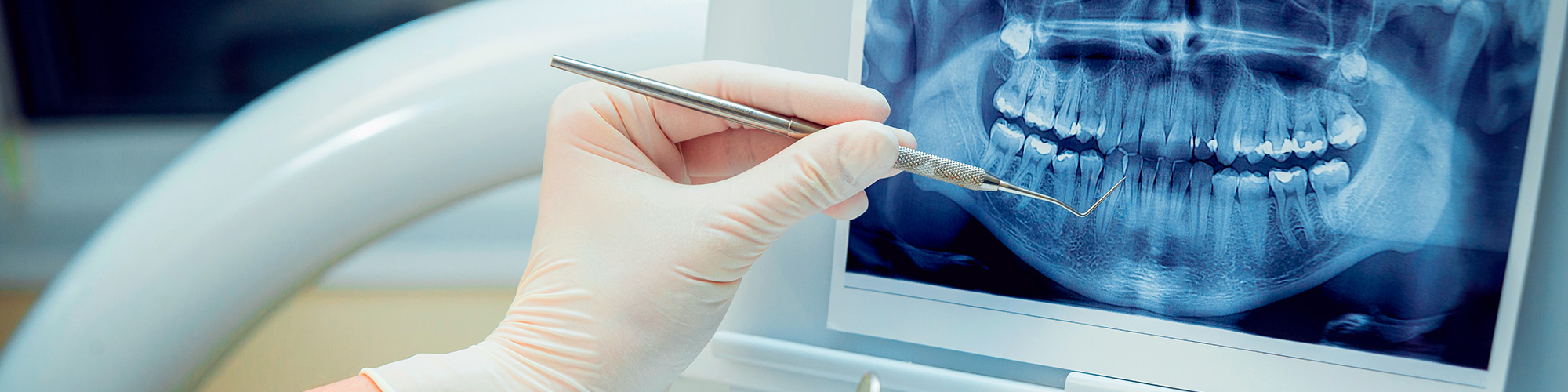
Conservative Dentistry
Conservative dentistry is a branch of dentistry that deals with the restoration of the hard tissues of teeth that may have been destroyed by the following causes:
- Trauma.
- Alterations and/or modifications in tooth development, producing more fragile enamel or dentine.
- Cavities.
Dental caries is a multifactorial disease characterised by the destruction of tooth tissues due to demineralisation caused by acids generated by plaque bacteria. Bacteria present in plaque make the acids that plaque generates.
Thus, it is also related to poor dental hygiene, non-flossing, as well as genetic aetiology and the influence of pH in saliva.
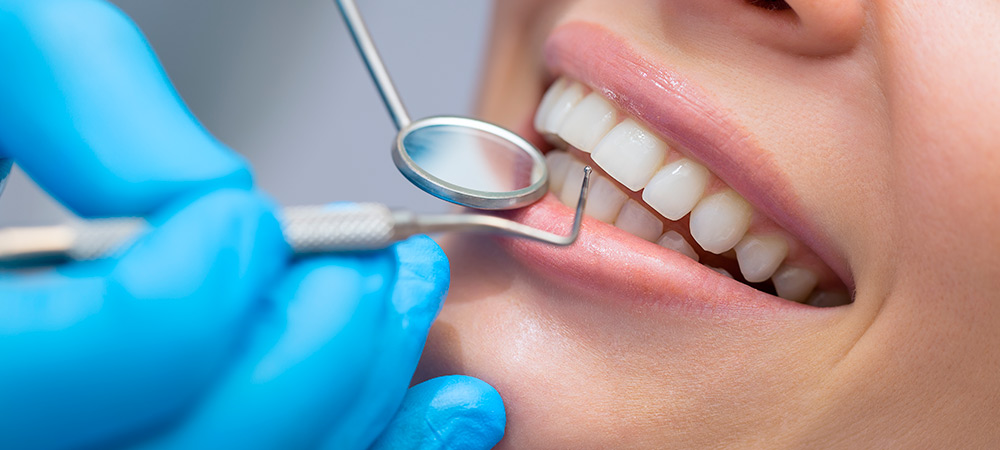
Cavities begin with the enamel decay, if it continues to progress, it reaches the dentine, and if left untreated, it can reach the dental pulp, causing inflammation (pulpitis) and subsequent necrosis (pulp death). If proper treatment is not carried out, the inflammation can reach the area surrounding the apex of the tooth (the area at the end of the dental root) producing what is called apical periodontitis.
Depending on the location of the cavity, the treatment can range from a simple filling or reconstruction to the nerve treatment, which is called endodontics. Let’s take a closer look at this type of treatment in the specific area of cavities.
- Filling: is the procedure by which the anatomy of a tooth that has been altered by the existence of a cavity is restored.
- Endodontics: consists in removing the dental pulp and then filling and sealing the pulp cavity with an inert material.
The main causes that originate and influence the appearance of cavities are related to three aspects: dietary, bacterial and the individual’s constitution.
- High-sugar diet: when we have a diet rich in sugars, bacteria take it as food and break it down, producing acids that directly attack the tooth enamel.
- Bacteria: are responsible for fermenting sugars.
- Anatomy of the tooth itself: i.e. the shape and distribution of the dentition, which can make certain points of the tooth a potential source of cavities.
Some of the keys to preventing cavities are as follows:
- Good oral hygiene.
- Brush teeth three times a day or after every meal.
- Flossing.
- Using fluoride-containing toothpaste.

